Introduction to Pipe Fittings
Pipe fittings are essential components used to connect, redirect, extend, or terminate pipelines in plumbing, irrigation, oil & gas, and firefighting systems. Without fittings, pipes cannot be efficiently joined or adapted to different requirements like direction change, size adjustment, or pressure handling.
In industrial engineering, pipe fittings ensure fluid flow is safe, leak-proof, and meets international standards. From elbows and tees to reducers, flanges, and puddle flanges, fittings are designed in multiple shapes, materials, and connection methods.
This guide covers:
- Types of fittings (items)
- Materials used (metallic & non-metallic)
- Connection methods (threaded, welded, flanged, etc.)
- Applications (plumbing, firefighting, irrigation, oil & gas)
- Standards & classifications (IS, ASTM, DIN, JIS)
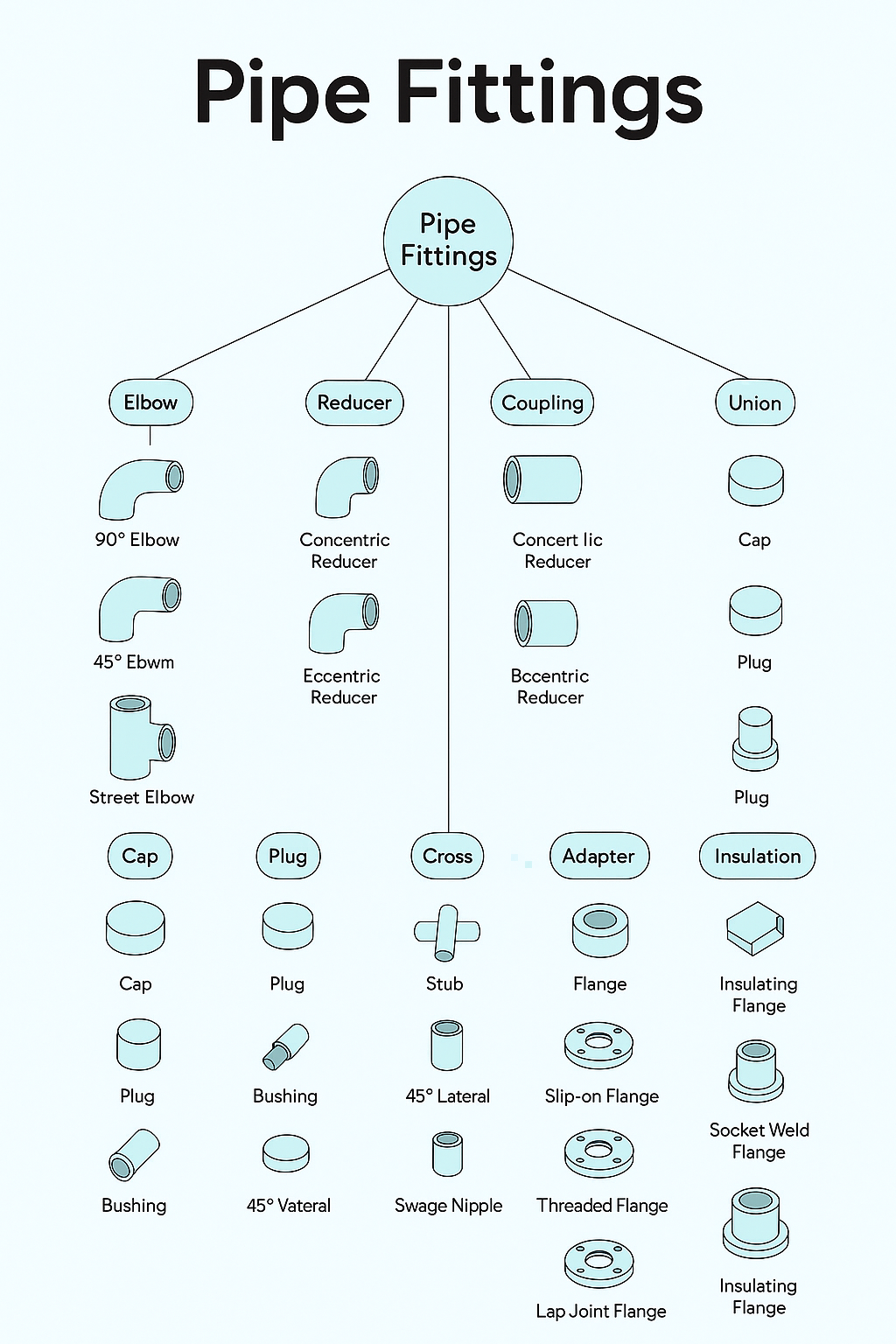
Types of Pipe Fittings (Items)
Pipe fittings come in various shapes, each serving a unique purpose.

Elbow Fittings
Elbows change the direction of flow.
180° Return Bend – Flow reversal in U-shaped form.
90° Elbow – Sharp right-angle turn.
45° Elbow – Gentle flow change.
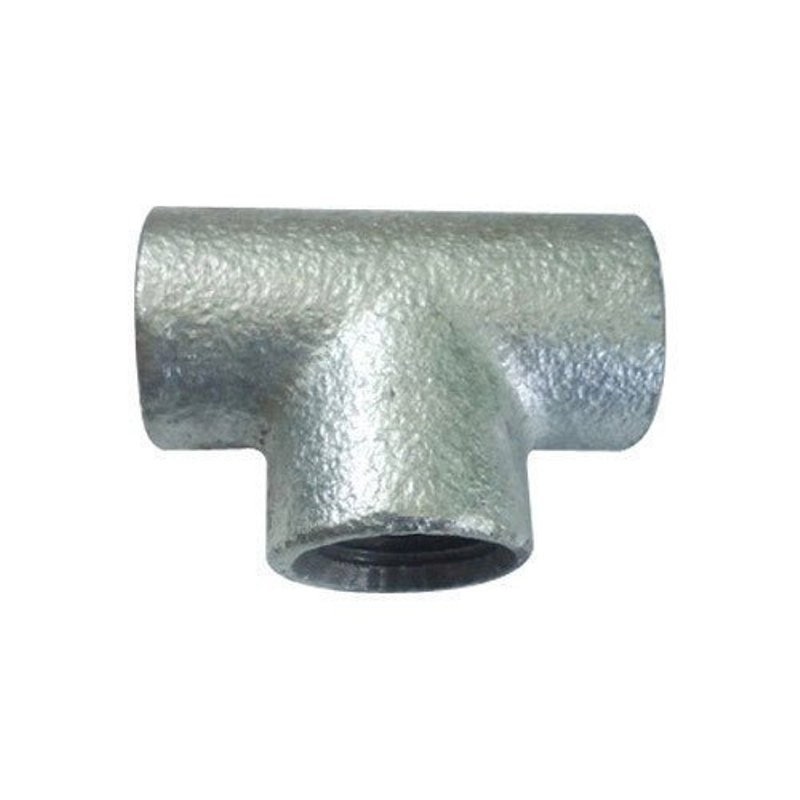

Tee Fittings
Tees split or combine flow.
Reducing Tee – Branch of smaller size.
Equal Tee – Same size openings.
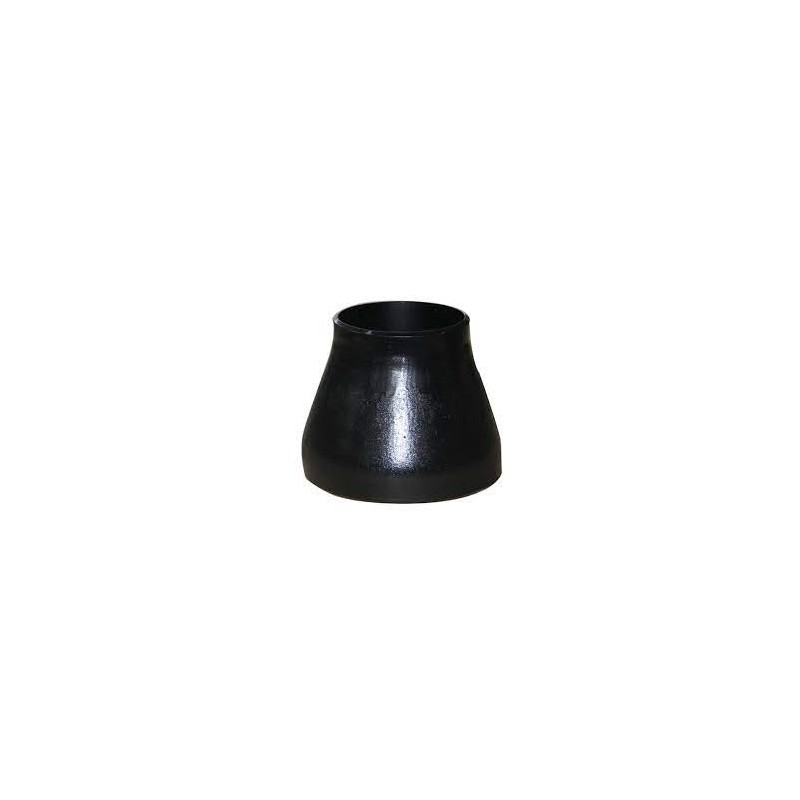

Reducer Fittings
Reducers adjust pipe diameter.
Eccentric Reducer – Offset reduction for drainage systems.
Concentric Reducer – Aligned reduction for balanced flow.
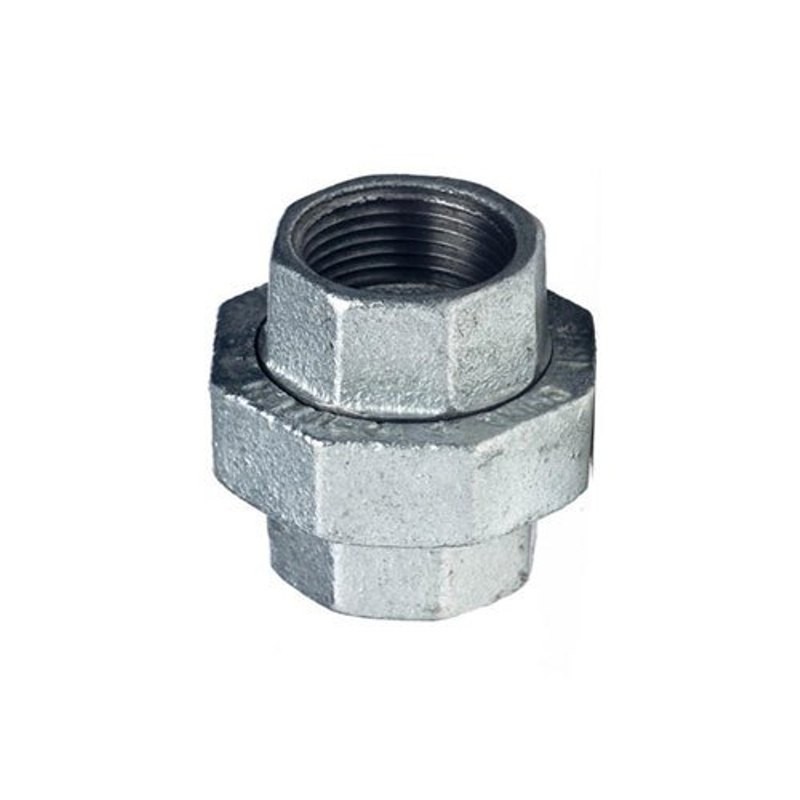

Union Fittings
Allow easy dismantling without cutting. Commonly used in pipelines needing maintenance.
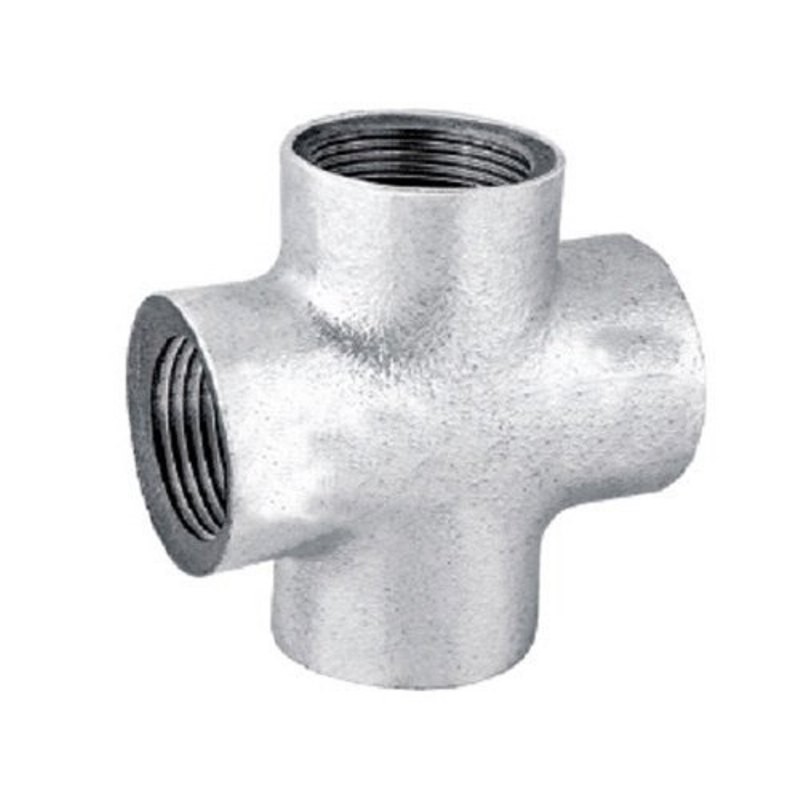

Cross Fittings
Reducing Cross – One or more branches smaller.
Equal Cross – Four outlets of same size.
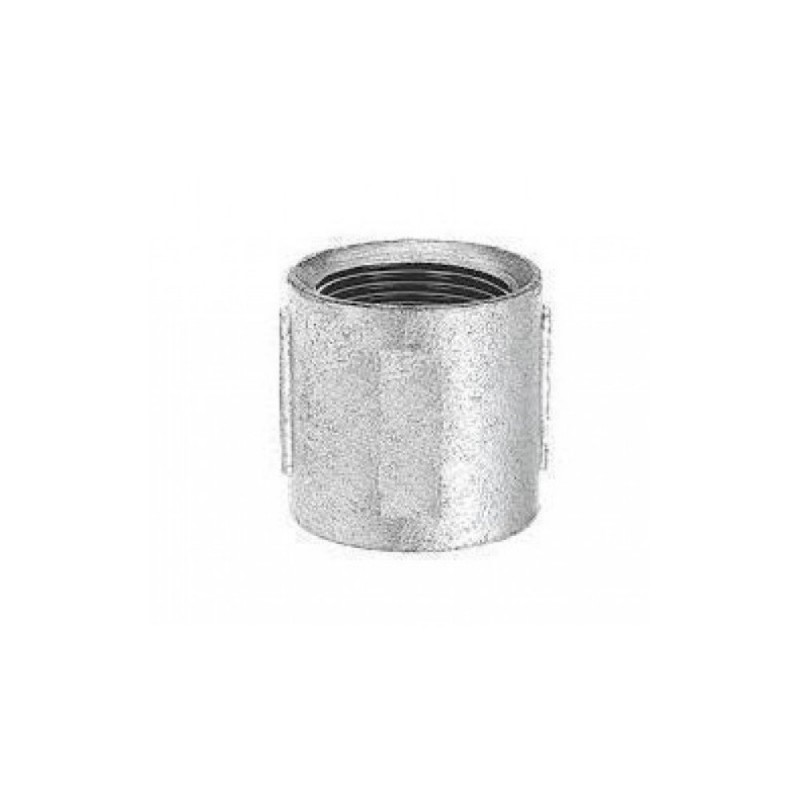

Socket Fittings
Used for small bore piping.
Socket Weld
Plain Socket
Reducing Socket

Flange Fittings
Flanges connect pipes with bolts.
Threaded Flange
Weld Neck Flange
Blind Flange
Slip-On Flange

Puddle Flange
Installed where pipes pass through concrete walls to prevent leakage.
HDPE Puddle Flange
MS Puddle Flange
SS Puddle Flange
GI Puddle Flange
Materials Used in Pipe Fittings
Pipe fittings are classified into metallic and non-metallic categories.
Metallic Materials
- Mild Steel (MS) – Cost-effective, widely used in water supply & fabrication.
- Stainless Steel (SS 304, SS 316) – Corrosion-resistant, preferred in oil & gas, chemical, and food industries.
- Brass & Copper – High thermal conductivity, plumbing use.
- Cast Iron / Ductile Iron – Strong, used in sewage & drainage systems.
Non-Metallic Materials
- PVC & CPVC – Lightweight, plumbing & drainage.
- HDPE – Flexible, high pressure resistance.
- PPR / PP – Hot & cold water supply systems.
Pipe Fitting Connections
Pipe fittings are connected by different joining techniques:
- Threaded – Screwed ends, easy for small bore pipelines.
- Welded – Permanent, leak-proof, used in industries.
- Flanged – Bolted, easy maintenance, large pipelines.
- Compression – Mechanical sealing, no welding needed.
- Push Fit – Quick installation, mostly for non-metallic pipes.
Applications of Pipe Fittings
Pipe fittings are used across multiple industries:
- Plumbing & Domestic Water Supply – Elbows, tees, sockets, PVC/CPVC.
- Oil & Gas Industry – SS flanges, reducers, threaded joints.
- Firefighting Systems – GI fittings, puddle flanges, reducers.
- Irrigation & Agriculture – HDPE fittings, compression couplings.
Pipe Fitting Standards & Classifications
To ensure safety and quality, pipe fittings follow international standards.
- IS (Indian Standards – IS 1239, IS 1538)
- ASTM/ASME (American Standards – ASTM A234, ASME B16.9)
- DIN/EN (European Standards – DIN 2605, EN 10253)
- JIS (Japanese Standards – JIS B2311, B2312)
How to Select the Right Pipe Fitting
- By Size & Dimension (OD, NB, thickness).
- By Pressure Class (150#, 300#, etc.).
- By Material (MS, SS, HDPE).
- By Application (oil, water, firefighting).
- By Standard (IS, ASTM, JIS).
Conclusion
Pipe fittings are the backbone of plumbing and industrial pipelines. From elbows and tees to reducers, flanges, and puddle flanges, every fitting serves a unique function. Selecting the right material, connection type, and standard ensures durability and safety.